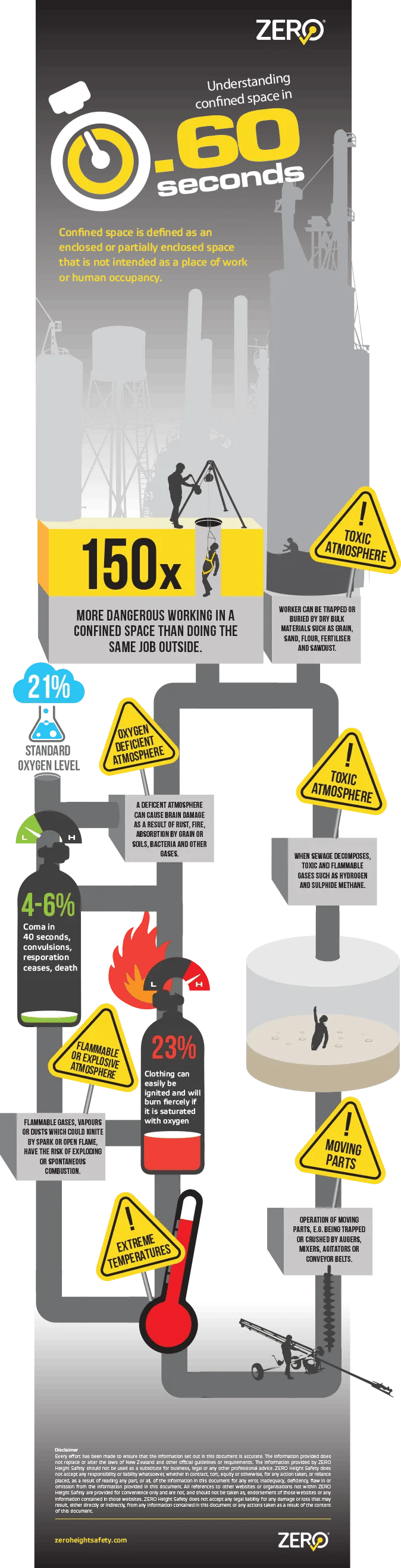
Working in confined spaces poses unique challenges. These environments can include storage tanks, silos, tunnels, and other enclosed areas. The potential hazards within confined spaces, such as lack of oxygen, toxic gases, and physical entrapment and falls require the use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to mitigate risks.
When working in confined spaces, the correct selection and utilisation of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential for the safety workers operating within these challenging environments. By understanding the specific hazards within these environments and following proper guidelines for PPE selection, fit, and usage, employers can mitigate risks effectively. Regular training, awareness programs, and consistent equipment inspections are crucial elements in maintaining a safe working environment in confined spaces.
It is crucial to identify and understand the potential hazards associated with confined spaces. Lack of oxygen, toxic or flammable gases, extreme temperatures, limited visibility, and the risk of physical entrapment are common dangers that workers may encounter. These hazards can result in asphyxiation, poisoning, falls, or serious injuries if preventive measures are not in place.
The Role of Personal Protective Equipment
PPE serves as the first line of defense against the potential risks present in confined spaces. By wearing the correct PPE, workers can safeguard themselves from the identified hazards and perform their tasks with greater confidence. The key types of PPE relevant to working in confined spaces include:
Respiratory Protection
Due to the risk of oxygen deficiency or toxic gas exposure, respiratory protection is vital. Depending on the specific environment, workers may need to wear self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA), air-purifying respirators, or supplied-air respirators.
Protective Clothing
Clothing must be selected based on the specific hazards involved. This can include flame-resistant coveralls, chemical-resistant suits, or high-visibility apparel. The clothing should be durable, properly fitted, and designed to minimize the risk of entanglement.
Head and Eye Protection
An industrial helmet with a rated chin straps and multi-impact protection are essential to protect during a fall or for falling objects to prevent serious head injuries. Safety goggles, visors or full face face shields must also be worn to shield the eyes from debris, chemicals, or intense light.
Hand and Foot Protection
Workers should utilize appropriate gloves to protect against cuts, burns, or chemical exposure. Additionally, safety boots or shoes with reinforced toes and slip-resistant soles should be worn to prevent foot injuries.
Selecting the Correct PPE
The selection of PPE should be based on a thorough assessment of the confined space and its associated hazards. Here are some key considerations:
Conduct a Risk Assessment
Identify the potential hazards and evaluate the level of risk associated with each. This assessment will help determine the specific types of PPE needed.
Consult Safety Guidelines and Regulations
Refer to local safety regulations and industry standards to ensure compliance and to obtain guidance on suitable PPE for confined spaces.
Perform Fit Testing
PPE, especially respiratory protective equipment, must be properly fitted to ensure effective protection. Fit testing should be conducted regularly to verify the equipment's suitability and worker's safety.
Training and Awareness
Using the correct PPE is crucial, but it is equally important to provide thorough training and raise awareness among workers. Training programs should cover the proper use, maintenance, and limitations of PPE. Additionally, workers must be educated on emergency procedures, communication protocols, and the importance of constant vigilance in confined spaces.
Protection from Falling Hazards in Confined Spaces
Working in confined spaces can pose various risks, including the danger of falling from heights. It is essential to use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for fall protection. The most critical considerations for ensuring safety against falling hazards are fall arrest systems, anchorage points, safety lanyards, self-retracting lifelines, guardrails and barriers, training and competence, regular inspections, and compliance with regulations. Workers must be provided with comprehensive training on the proper use, inspection, and maintenance of fall protection equipment, including identifying fall hazards, understanding rescue procedures, and knowing when and how to use provided PPE. By implementing the appropriate PPE for fall protection, workers can significantly reduce the risk of injuries or fatalities associated with confined spaces' falling hazards.
The following are key considerations for ensuring safety in relation to falling hazards:
Fall Arrest Systems
When working at heights or in areas with potential fall risks, a fall arrest system should be employed. This includes a full-body harness, lanyards, and anchor points. The harness should be correctly fitted and regularly inspected for any signs of wear or damage.
Anchorage Points
Properly installed anchor points or lifelines are essential for connecting the fall arrest system. These anchor points must be sturdy, able to support the expected load, and strategically located to provide maximum protection.
Safety Lanyards and Self-Retracting Lifelines (SRLs)
Safety lanyards and SRLs are used to connect the harness to the anchor point. These devices should be chosen based on the specific requirements of the confined space, taking into account the length, type, and shock-absorbing capacity.
Guardrails and Barriers
In some cases, the use of physical barriers, guardrails, or toe-boards may be necessary to prevent falls from elevated platforms or edges. These protective measures should be securely installed and regularly inspected for stability.
Training and Competence
Workers must receive comprehensive training on the proper use, inspection, and maintenance of fall protection equipment. They should be proficient in identifying fall hazards, understanding rescue procedures, and knowing when and how to use the provided PPE.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
PPE for fall protection should undergo routine inspections to ensure that all components are in good working condition. Any damaged or worn-out equipment must be replaced promptly.
Compliance with Regulations
It is essential to adhere to relevant safety regulations and industry standards regarding fall protection. Familiarize yourself with local guidelines and ensure that all PPE and safety measures meet or exceed the required standards.
Working in confined spaces demands strict adherence to safety protocols and the use of appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to mitigate potential hazards. The selection of PPE should be based on a thorough assessment of the confined space and its associated hazards, as well as compliance with local safety regulations and industry standards. By implementing the correct PPE, workers can significantly reduce the risk of injuries or fatalities associated with confined space operations. It is essential to regularly inspect and maintain PPE and stay current with relevant safety regulations and industry standards.
Check out our infographic that identifies some of the hazards associated with working in confined spaces.